Have you ever stopped to think about the tiny, unseen parts that make up every living thing? It's really quite something to consider how much activity goes on in a space so small you can't even see it with your eyes alone. Cells, the very building blocks of life, are packed with all sorts of miniature structures, each doing its own very important job. It's almost like a tiny, bustling city, with different areas handling different tasks to keep everything running smoothly.
One of the most significant parts within many of these microscopic structures is what we call the nucleus. This particular part is, you know, often thought of as the command center, the place where all the big decisions get made for the cell's daily operations. It holds the vital instructions that tell the cell how to grow, how to divide, and what functions it needs to carry out. Without this central hub, things would get quite messy, pretty much right away.
Picture a busy office where all the important files and blueprints are kept in one main area, guiding everyone's work. That's a bit like what the nucleus does for a cell. It’s where the cell’s most precious cargo, its genetic information, is carefully stored and managed. We're going to take a closer look at this fascinating part of the cell, exploring what it does and why it's so absolutely central to life as we know it, perhaps even imagining what a clear, moving image, a sort of nucleus GIF, might show us about its inner workings.
- Aidy Bryant Husband
- Nia Nacci Retired
- Paul Mccartney Wives
- Patrick Mahomes Family Dynamics
- Tony Goldwyn And Wife
Table of Contents
- What's Inside a Nucleus and How Does It Look in a Nucleus GIF?
- Why is the Nucleus So Important for Life?
- Do All Cells Have a Nucleus?
- What About Human Cells and Their Nucleus?
What's Inside a Nucleus and How Does It Look in a Nucleus GIF?
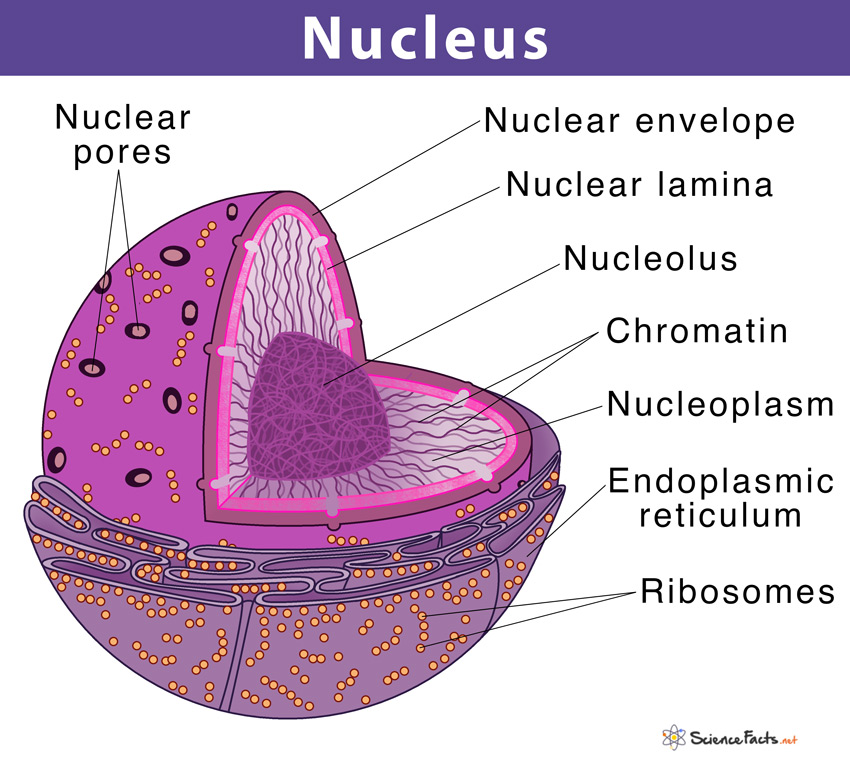
When you peer into the heart of a cell, or perhaps see a detailed representation that functions a bit like a nucleus GIF, you'd notice that the nucleus isn't just an empty space. It's actually quite packed with important components. One of the main things you'd find inside is something called chromatin. This chromatin is, you know, a very special substance, made up of the cell's DNA along with various proteins that are closely connected to this genetic material. Think of it as the cell's entire instruction manual, bundled up and carefully stored away. These proteins help organize the long strands of DNA, making sure they don't get tangled and are ready to be read when the cell needs to access specific bits of information. It's a very organized system, actually, ensuring that every piece of the genetic code is accessible but also protected from harm.
The DNA itself holds all the blueprints for making new proteins, which are the workhorses of the cell, carrying out almost every function imaginable. So, the chromatin, with its DNA and helper proteins, is truly at the core of what makes a cell what it is. If you were to create a nucleus GIF to show this, you might see these long, thread-like structures moving and shifting, sometimes coiling up tightly, other times loosening a bit, depending on what the cell is doing at that moment. It's a dynamic environment, always in motion, even though it's all happening on a scale that is just incredibly small. The way these parts interact is a pretty amazing thing to observe, even in a simulated form. The sheer amount of information held within this tiny space is truly remarkable, and the way it's managed speaks volumes about the cell's intricate design.
The Nuclear Envelope and a Nucleus GIF
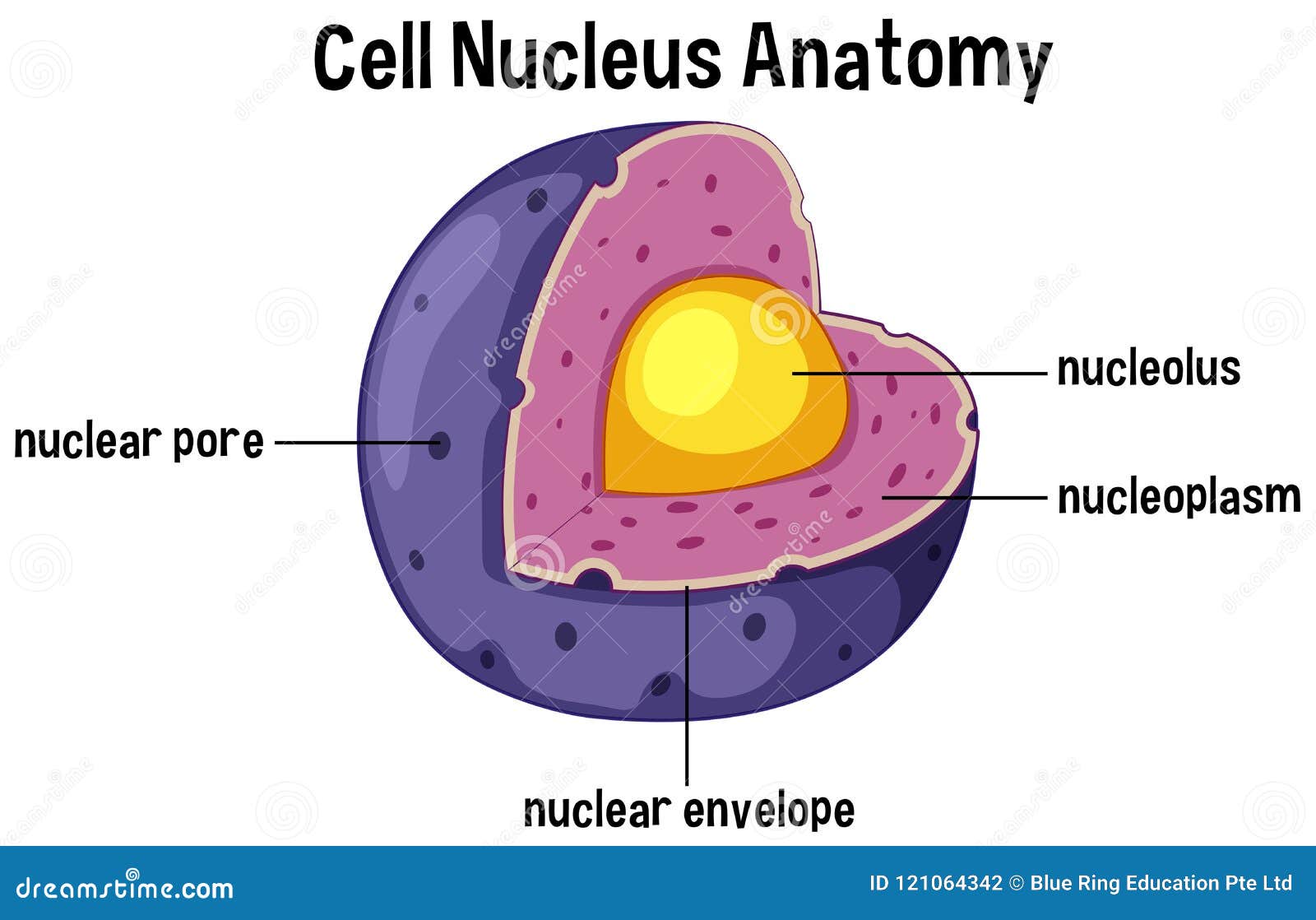
Now, this precious internal content, the chromatin and everything else inside the nucleus, isn't just floating around freely. It's actually, you know, protected by a very important boundary. This boundary is known as the nuclear envelope. It's not just a single layer; rather, it's a double membrane, almost like having two protective walls around a very important vault. This double layer helps to keep the cell's genetic material separate from the rest of the cell's fluid, or cytoplasm, which is where many other activities take place. If you were looking at a nucleus GIF, you might see this boundary as a distinct, somewhat porous outer shell, clearly setting apart the nucleus from its surroundings. It's a very clear dividing line, separating the central control room from the bustling factory floor.
- Elisabeth Chalier
- Ray Romano Bio
- Jade Cargills Family Life
- Who Is Joan Cusacks Husband
- Cancer Sagittarius Compatibility
The nuclear envelope isn't just a passive barrier, though. It has tiny openings, called nuclear pores, which act like gateways. These small openings allow certain materials to pass in and out of the nucleus, while keeping others out. For example, messages from the DNA need to leave the nucleus to tell other parts of the cell what to do, and various building blocks need to come in. So, these pores are absolutely vital for communication between the nucleus and the rest of the cell. A good nucleus GIF might even show these pores as little channels, with molecules zipping through them, illustrating the constant flow of information and materials. It's a highly regulated system, ensuring that only the right things get in and out, which is pretty important for maintaining order and proper cell function. The integrity of this envelope is also critical for protecting the genetic information from damage that could occur from the activities outside its walls.
Why is the Nucleus So Important for Life?
So, why all this fuss about a tiny structure within a cell? Well, the nucleus plays a role that is just, you know, truly central to the existence and operation of nearly all complex life forms. In cells that possess a nucleus, known as eukaryotic cells, the DNA, which carries all the instructions for life, is found primarily within this special compartment. This means that the nucleus serves as the main storage facility for the cell's genetic blueprint. Without it, the cell wouldn't have a centralized place to keep its most valuable information, and that would create a whole host of problems for the cell's ability to function correctly. It’s like having a library where all the books are scattered everywhere instead of being neatly organized and protected.
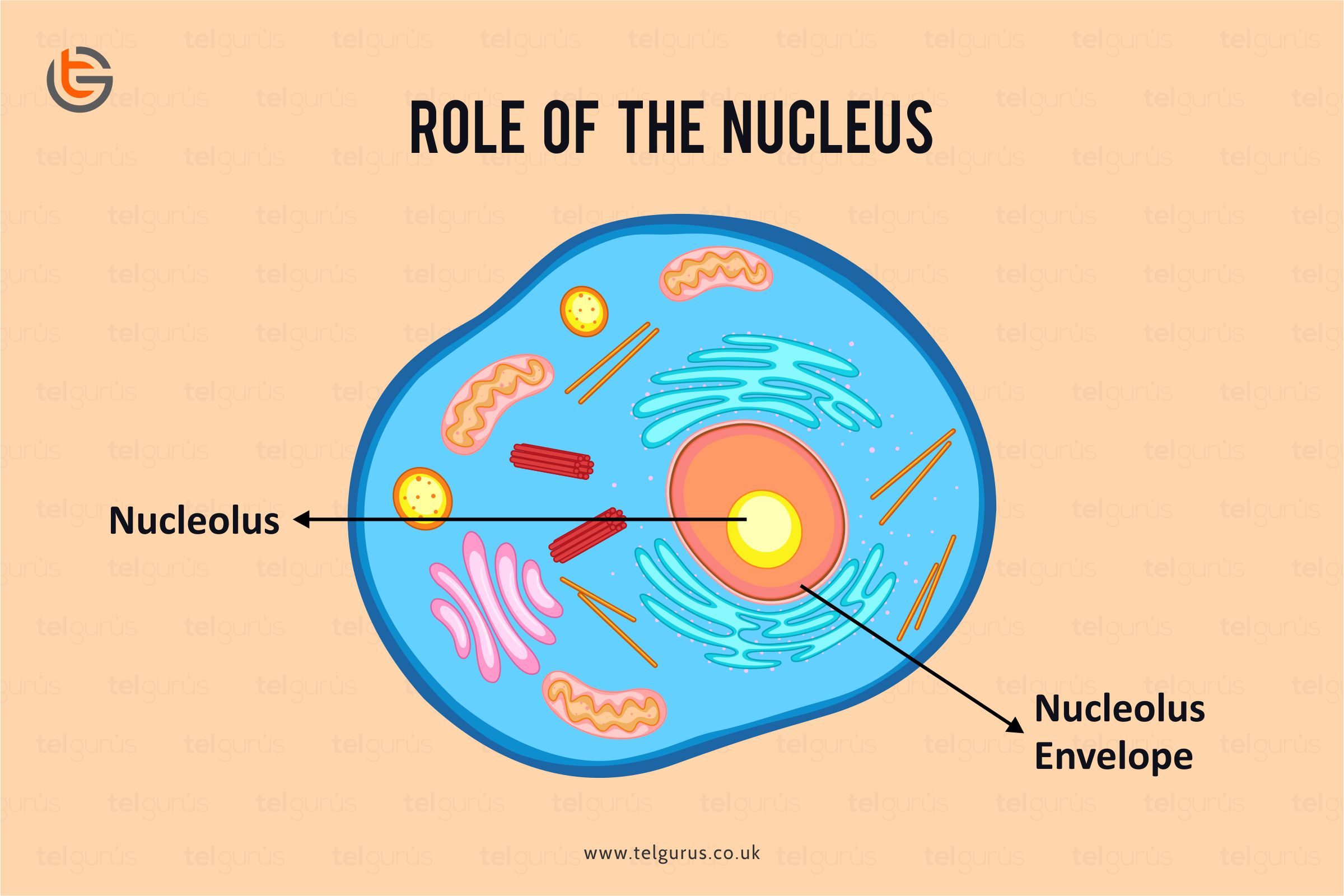
Beyond just holding the genetic information, the nucleus acts as the cell's control center, or perhaps you could say, its main office. It houses the vast majority of the cell's genetic material, and this material is what dictates how the cell operates. It’s responsible for regulating what genes are turned on or off, which in turn controls how cells grow, how they divide to make new cells, and what specific jobs they perform. For instance, a muscle cell needs different instructions than a skin cell, and the nucleus makes sure the right instructions are followed at the right time. This level of oversight is, you know, pretty much what allows a complex organism, like a person, to develop and maintain all its different tissues and organs. It's a constant process of management and direction, ensuring everything stays on track.
The Nucleus- A Cell's Command Center and a Nucleus GIF
To put it simply, the nucleus is the absolute command center of a cell. It's the place that directs all the cellular activity, telling other parts of the cell what to do and when to do it. It's also where all the hereditary information, the stuff passed down from one generation to the next, is stored. This means it holds the instructions for everything from eye color to how your heart beats. If you were to visualize this with a nucleus GIF, you might see a flurry of activity within its walls, with messages being sent out and received, all contributing to the cell's overall behavior. It's a very dynamic place, despite its seemingly static appearance when viewed through a microscope. The constant communication and direction from this central point are what allow cells to respond to their environment and carry out their specialized roles. This central direction is, you know, absolutely key for the cell's survival and for the proper functioning of the entire organism it belongs to.
Within the nucleus, there's also a very special structure called the nucleolus. This particular part is primarily involved in the production and assembly of ribosomes. Ribosomes are, you know, little cellular machines that are absolutely essential for making proteins, which, as we mentioned, are the workhorses of the cell. So, in a way, the nucleolus is like a small factory within the main control center, churning out the parts needed for protein creation. A nucleus GIF might highlight the nucleolus as a denser, darker spot within the nucleus, perhaps even showing tiny components being put together there. This shows just how many layers of organization exist even within this one central organelle. The entire process, from the genetic instructions to the final protein, is a testament to the cell's incredible design and efficiency, all orchestrated from the nucleus. It’s quite amazing how all these pieces fit together so perfectly.
Do All Cells Have a Nucleus?
That's a very good question, and the answer is, you know, actually no, not every single cell has a nucleus. While many cells, especially those that make up plants, animals, and fungi, do have this central control room, there's a whole category of cells that simply don't. These are known as prokaryotic cells. Think of them as the simpler, more ancient forms of life. Bacteria and archaea are the main examples of prokaryotic cells. They are single-celled organisms, and their internal structure is much less complex than cells with a nucleus. They still have genetic material, of course, because every living thing needs instructions, but it's not enclosed within a separate compartment. Instead, their DNA is usually found in a region within the cell's main body, often in a somewhat centralized area, but without a surrounding membrane. This difference in organization is a pretty fundamental distinction in the world of biology.
The lack of a nucleus in prokaryotic cells means that their cellular processes are organized differently. Without that central command center, the genetic material is directly accessible to the cell's machinery that reads the instructions and makes proteins. This can actually make their processes quite fast and efficient in some ways, allowing them to adapt and reproduce quickly. However, it also means they generally can't achieve the same level of complexity or specialization as eukaryotic cells. So, while they are incredibly successful life forms, thriving in almost every environment on Earth, their internal layout is, you know, a bit more straightforward. It’s a completely different way of managing the cell's operations, showing the diversity of life's solutions to basic biological problems. It's a fascinating contrast, really, between two very successful cellular designs.
Prokaryotic Cells and Lacking a Nucleus GIF
If you were to look at a representation, perhaps a nucleus GIF that also shows prokaryotic cells for comparison, you would immediately see the absence of that distinct, rounded structure in the middle. Instead, you might see the genetic material, which is often a single, circular piece of DNA, simply floating within the cell's cytoplasm. There's no separate boundary or double membrane enclosing it. This difference is a really key visual identifier when comparing these two major cell types. It highlights how some life forms manage their genetic information without the need for a dedicated, walled-off control center. The simplicity of their internal organization is, you know, one of their defining characteristics. This doesn't make them less effective, just different in their approach to cellular architecture. Their smaller size and simpler structure allow them to reproduce very quickly, which is a major advantage in many environments. It’s a testament to how life finds many ways to thrive, even without certain components we might consider essential in other contexts.
The machinery for making proteins, the ribosomes, are also present in prokaryotic cells, but they are scattered throughout the cytoplasm, not produced in a specialized nucleolus. This means that the processes of reading the DNA and making proteins can happen almost simultaneously, which contributes to their rapid growth and division. So, while they don't have a nucleus, they certainly have their own highly effective system for managing their genetic information and carrying out all the necessary life functions. A good visual, even a conceptual nucleus GIF comparison, would really help illustrate these fundamental differences in cellular design. It truly shows how diverse the solutions are in biology for achieving the same basic goals of life, growth, and reproduction. It's a pretty neat trick that these tiny cells pull off every single day.
What About Human Cells and Their Nucleus?
When we talk about human cells, we are definitely talking about eukaryotic cells. This means that every single one of your cells, from your skin cells to your brain cells, contains a nucleus. It's a pretty fundamental feature of our biology. Within these human cells, the nucleus is where the vast majority of our DNA is stored. This DNA is, you know, incredibly important, as it contains all the instructions that make you, well, you. It tells your cells how to grow, how to repair themselves, and how to perform their specific duties. Without a nucleus, our complex bodies simply wouldn't be able to function, let alone develop from a single fertilized egg. It's the central repository for all the genetic information that defines us as a species and as individuals. The organization provided by the nucleus is absolutely essential for the intricate processes that happen within our bodies every second of every day.
Besides the nucleus, human cells also have other specialized parts, called organelles, that perform different jobs. For example, we have mitochondria, which are often called the "powerhouses" of the cell because they generate most of the energy the cell needs to do its work. But it's the nucleus that really organizes the DNA and makes sure the right instructions are available at the right time. It’s like the main office that keeps all the important documents in order, while other departments handle production or energy. The information about cell structures, particularly the nucleus, helps us understand how our bodies are built and how they manage to perform such a wide range of complex functions. The nucleus, with its organized genetic material, is, you know, truly at the heart of what makes human life possible, guiding every single cellular process with precision. It's a remarkably efficient system that has evolved over a very long time.
The Nucleolus- A Key Part of the Nucleus and a Nucleus GIF
As we mentioned earlier, inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, including our own human cells, you'll find a distinct structure called the nucleolus. This part is, you know, quite prominent, often appearing as a denser spot within the nucleus itself. While the nucleus is the overall command center, the nucleolus has a very specific and absolutely vital role: it's primarily involved in the production and assembly of ribosomes. Ribosomes, as you might recall, are the tiny cellular factories responsible for creating proteins based on the instructions from the DNA. So, in essence, the nucleolus is like the ribosome assembly line within the nucleus, making sure the cell has enough of these protein-making machines to carry out all its functions. If you could see a detailed nucleus GIF, you would observe this area as a hub of intense activity, with components coming together to form these crucial protein builders.
The process that happens in the nucleolus is pretty intricate. It involves synthesizing ribosomal RNA, or rRNA, which is a key component of ribosomes, and then combining it with specific proteins to build the ribosomal subunits. These subunits then leave the nucleus and come together in the cytoplasm to form functional ribosomes. So, while the DNA in the main part of the nucleus holds the blueprints for all proteins, the nucleolus is specifically focused on creating the tools needed to read those blueprints. This division of labor within the nucleus itself is, you know, another example of the cell's incredible efficiency and organization. It ensures that the cell always has a steady supply of ribosomes, which are constantly needed for growth, repair, and all the daily operations that keep a cell alive and healthy. It's a testament to the cell's remarkable internal structure and coordination.
The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell, and for very good reason. It houses the cell's genetic material, directs cellular activity, and ensures that the right instructions are followed for growth, division, and function. This remarkable organelle, with its protective nuclear envelope and its specialized nucleolus, is truly at the heart of eukaryotic life. From regulating gene expression to storing hereditary information, the nucleus is a constant manager, ensuring the cell operates smoothly and efficiently. It’s a very intricate and well-organized system, really, that plays an absolutely vital role in every living thing that possesses one.
Related Resources:
Detail Author:
- Name : Stephany Upton
- Username : gaylord.oswaldo
- Email : mateo.becker@gutmann.com
- Birthdate : 1998-10-02
- Address : 448 Myra Circles Rachelbury, WA 95158-5912
- Phone : +1 (520) 930-3444
- Company : Torphy, Donnelly and Jerde
- Job : Record Clerk
- Bio : Dolor corrupti ut ab ratione consequatur. Sit est illo sit. Sunt voluptatum minima qui ipsa minus velit autem. Asperiores rerum odit assumenda atque facilis et.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/lowe2011
- username : lowe2011
- bio : Recusandae sed quia recusandae doloremque.
- followers : 1597
- following : 1911
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/lowe2009
- username : lowe2009
- bio : Nihil aliquid rerum quasi dolores. At et neque non. Recusandae excepturi sapiente commodi expedita natus. Quia maxime sed doloribus ut ut aspernatur provident.
- followers : 1267
- following : 1939
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/hildegard1591
- username : hildegard1591
- bio : Vel et est sed ut.
- followers : 3153
- following : 1656
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/hlowe
- username : hlowe
- bio : Sed unde at impedit. Earum voluptas aut velit maiores aliquid. Quia aspernatur et asperiores et.
- followers : 5387
- following : 571